Widespread corruption refers to the pervasive and systemic misuse of power or position for personal or organizational gain, affecting multiple sectors within a society or country. It often undermines trust, economic stability, and governance.
Types of Corruption
- Political Corruption:
- Involves government officials abusing their power for personal gain, such as bribery, embezzlement, or electoral fraud.
- Corporate Corruption:
- Includes unethical practices within businesses, such as insider trading, fraud, or exploiting loopholes.
- Judicial Corruption:
- Judges or legal officials accepting bribes to alter rulings.
- Administrative Corruption:
- Misuse of public resources, such as favoritism in awarding contracts or demanding bribes for basic services.
Causes of Widespread Corruption
- Weak Governance:
- Lack of transparency and accountability in institutions.
- Economic Inequality:
- Poverty and income disparity can push individuals toward corrupt practices.
- Cultural Factors:
- Societal norms that tolerate or ignore corruption.
- Lack of Enforcement:
- Ineffective laws and institutions to curb corruption.
Impacts of Widespread Corruption
- Economic Consequences:
- Loss of public funds and investment.
- Stunted economic growth.
- Social Consequences:
- Erosion of trust in institutions.
- Increased inequality and social unrest.
- Political Consequences:
- Undermines democracy and rule of law.
- Leads to authoritarianism or failed states.
Examples of Widespread Corruption
- Global Examples:
- Corruption scandals in governments, such as embezzlement in Brazil’s Operation Car Wash.
- Corporate corruption, like the Enron scandal in the U.S.
- Everyday Examples:
- Bribery for accessing public services like healthcare or education.
- Nepotism in job hiring or promotions.
How to Combat Widespread Corruption
- Strengthening Institutions:
- Enforcing anti-corruption laws and ensuring transparency.
- Promoting Accountability:
- Whistleblower protection and public audits.
- Educating Citizens:
- Raising awareness about the costs of corruption.
- Leveraging Technology:
- Using digital systems to track public funds and reduce human interference.
Widespread corruption is a global issue that requires collective action from governments, organizations, and individuals to build fairer and more transparent societies.
Additional Insights
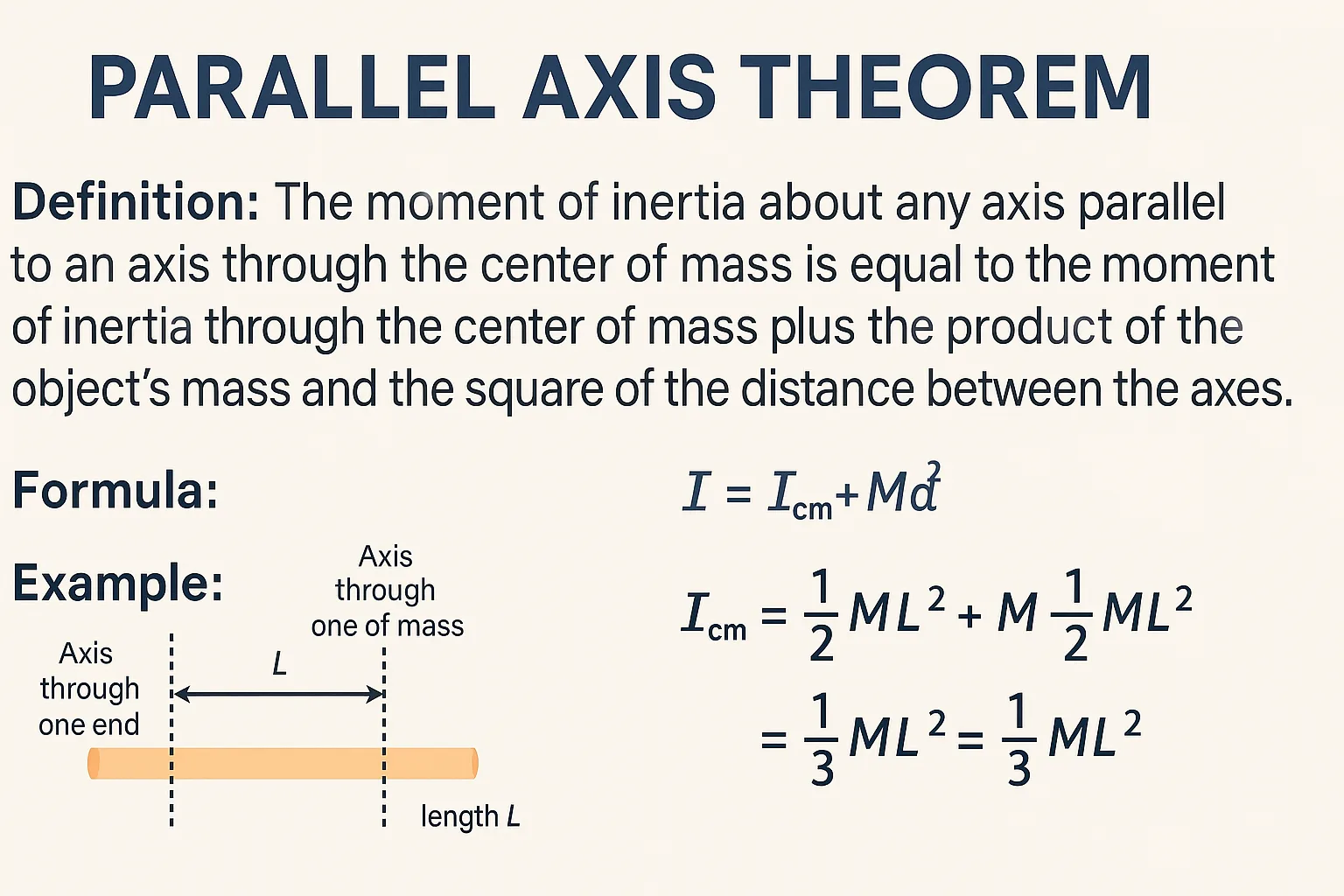
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
