The term “value” can be defined and understood in various contexts. Here’s a comprehensive definition and explanation of its meaning:
Definition of Value
Value refers to the importance, worth, or usefulness of something. It can be understood in several dimensions, including economic, moral, personal, cultural, and intrinsic aspects.
Meanings of Value
Economic Value:
Definition: The monetary worth of a good or service, determined by market dynamics such as supply and demand.
Example: The price of a product in a store reflects its economic value.
Moral or Ethical Value:
Definition: Principles or standards that guide behavior and decision-making regarding what is considered right or wrong.
Example: Values such as honesty, integrity, and compassion influence how individuals interact with others.
Personal Value:
Definition: Individual beliefs and priorities that shape a person’s actions and choices.
Example: A person may prioritize values like family, education, or health, which guide their life decisions.
Cultural Value:
Definition: Shared beliefs, practices, and norms that are significant to a particular group or society.
Example: Traditions, customs, and rituals that are important to a culture represent its values.
Intrinsic Value:
Definition: The inherent worth of something, independent of its utility or market price.
Example: Many people believe that nature has intrinsic value, regardless of its economic benefits.
Utility Value:
Definition: The usefulness or practical benefits of a good or service.
Example: A tool’s value may be assessed based on how effectively it performs its intended function.
Summary
In summary, value encompasses a wide range of meanings, from economic worth to moral principles and personal beliefs. It plays a crucial role in guiding individual behavior, shaping societal norms, and influencing decision-making across various aspects of life.
Additional Insights
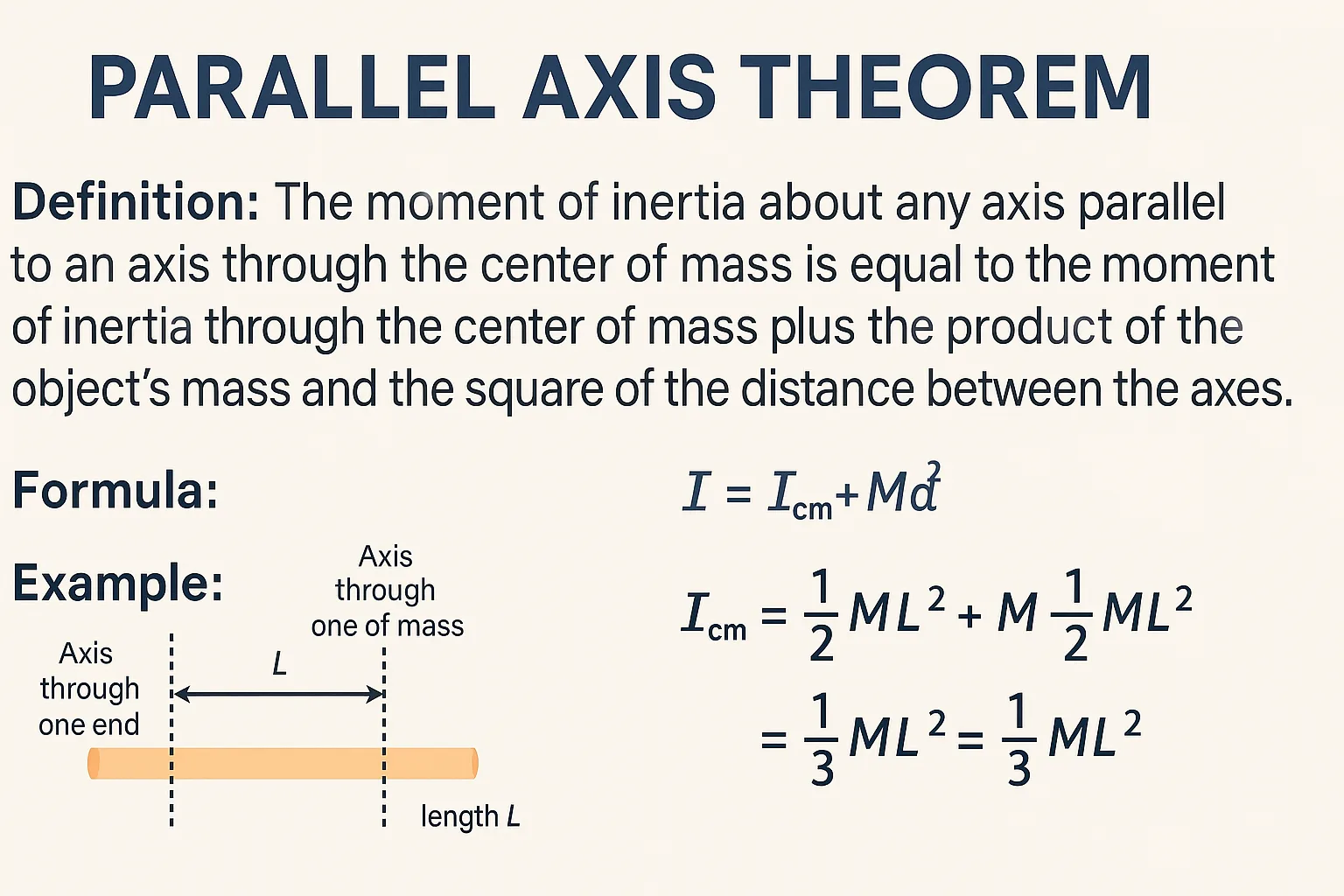
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
