Ficus carica (Common Fig)
Ficus carica is the botanical name for the common fig, a small deciduous tree or large shrub in the Moraceae family, native to the Mediterranean region and southwestern Asia. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, also called a fig.
Botanical Description
- Tree Characteristics:
- Height: Typically grows to 3–10 meters (10–33 feet).
- Trunk: Smooth, light gray bark.
- Branches: Spread wide, giving a bushy appearance.
- Leaves:
- Large, deeply lobed, and rough-textured, measuring 12–25 cm (5–10 inches) in length.
- Distinctive shape with 3–5 lobes.
- Fruit:
- Botanically a syconium, a hollow structure containing multiple tiny flowers.
- Shape: Pear-shaped.
- Color: Green when unripe, turning purple, black, or yellow when ripe.
- Pulp: Sweet and juicy, containing numerous tiny seeds.
- Flowers:
- Inconspicuous and located inside the syconium.
- Pollinated by fig wasps in wild varieties (mutualistic relationship).
Cultivation and Habitat
- Climate:
- Thrives in warm, temperate, and subtropical regions.
- Requires full sun and well-drained soil.
- Regions:
- Native to the Mediterranean Basin.
- Cultivated worldwide, including in the Middle East, California, India, and Australia.
- Propagation:
- Propagated through cuttings, suckers, or seeds.
Uses of Ficus carica
- Culinary:
- The fruit is consumed fresh, dried, or as a preserve.
- Used in desserts, salads, and baked goods.
- Nutritional Value:
- Rich in dietary fiber, vitamins (A, K, B-complex), and minerals (calcium, potassium, magnesium).
- Contains antioxidants.
- Traditional Medicine:
- Used as a remedy for digestive issues, respiratory problems, and inflammation.
- Horticulture:
- Grown as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes.
Interesting Facts
- One of the oldest cultivated plants, with a history dating back over 5,000 years.
- Considered sacred in some cultures, symbolizing fertility and abundance.
- The latex from the tree was traditionally used for medicinal purposes and to make cheese.
Ficus carica is a valuable plant both for its historical significance and its practical applications in food and medicine. Its adaptability and rich nutritional profile make it a beloved fruit around the world.
Additional Insights
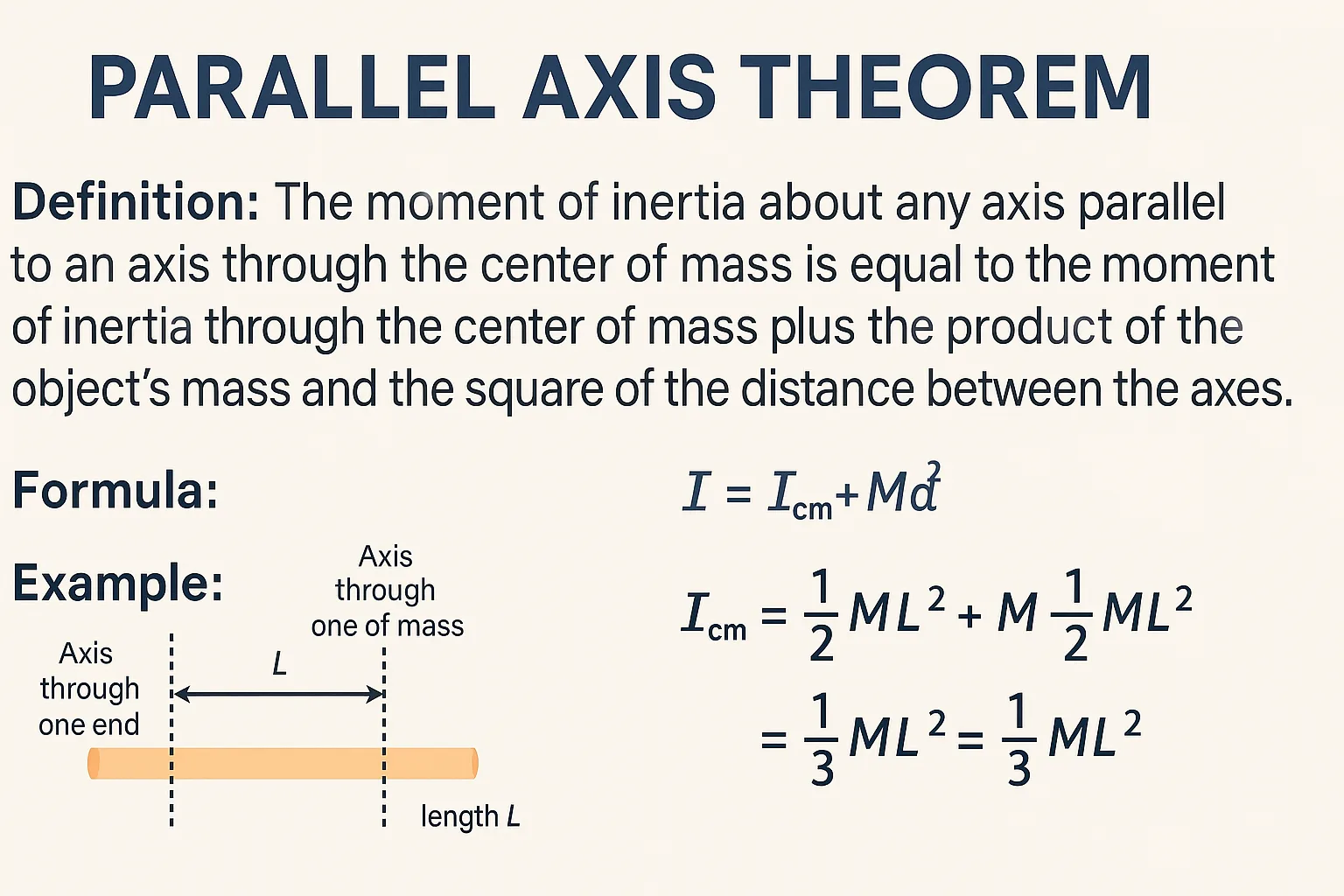
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
