Moraceae is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mulberry or fig family. This family includes a wide variety of trees, shrubs, and climbers that are found in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions around the world. Members of this family are known for their unique fruit structures, economic importance, and ecological roles.
Key Characteristics
- Growth Habits:
- Includes trees, shrubs, and vines.
- Many species exude a milky latex when cut.
- Leaves:
- Simple, alternate or opposite, and often have stipules.
- Deciduous or evergreen, depending on the species.
- Flowers:
- Unisexual (monoecious or dioecious).
- Small and inconspicuous, often grouped in clusters or inflorescences.
- Fruit:
- A characteristic feature is the multiple fruit formed from fused flowers, such as the fig (Ficus) and mulberry (Morus).
- Some species, like breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis), produce large, edible fruits.
Notable Genera and Species
- Ficus (Fig Trees):
- Includes the common fig (Ficus carica) and the fiddle leaf fig (Ficus lyrata).
- Known for their unique pollination relationship with fig wasps.
- Morus (Mulberries):
- Produces sweet, edible berries and is used in sericulture (silkworm farming).
- Artocarpus:
- Includes breadfruit and jackfruit, important staples in tropical regions.
- Broussonetia:
- Includes paper mulberry, historically used for making paper and textiles.
Economic and Ecological Importance
- Food Sources:
- Fruits like figs, mulberries, breadfruit, and jackfruit are widely consumed.
- Timber:
- Some species provide valuable wood for construction and furniture.
- Silk Production:
- Mulberry leaves are the primary food for silkworms in sericulture.
- Ecological Role:
- Many species are keystone plants, supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Fig trees, for example, sustain numerous wildlife species with their year-round fruiting.
Interesting Facts
- The family includes over 1,100 species in about 40 genera.
- Some species, like the banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis), are culturally significant and considered sacred in various traditions.
- Breadfruit has been a vital crop for Pacific Island communities for centuries, providing both food and cultural significance.
The Moraceae family showcases incredible diversity, with species that are integral to both ecosystems and human livelihoods. From providing food and shelter to being a symbol of cultural heritage, this plant family holds a special place in both nature and society.
Additional Insights
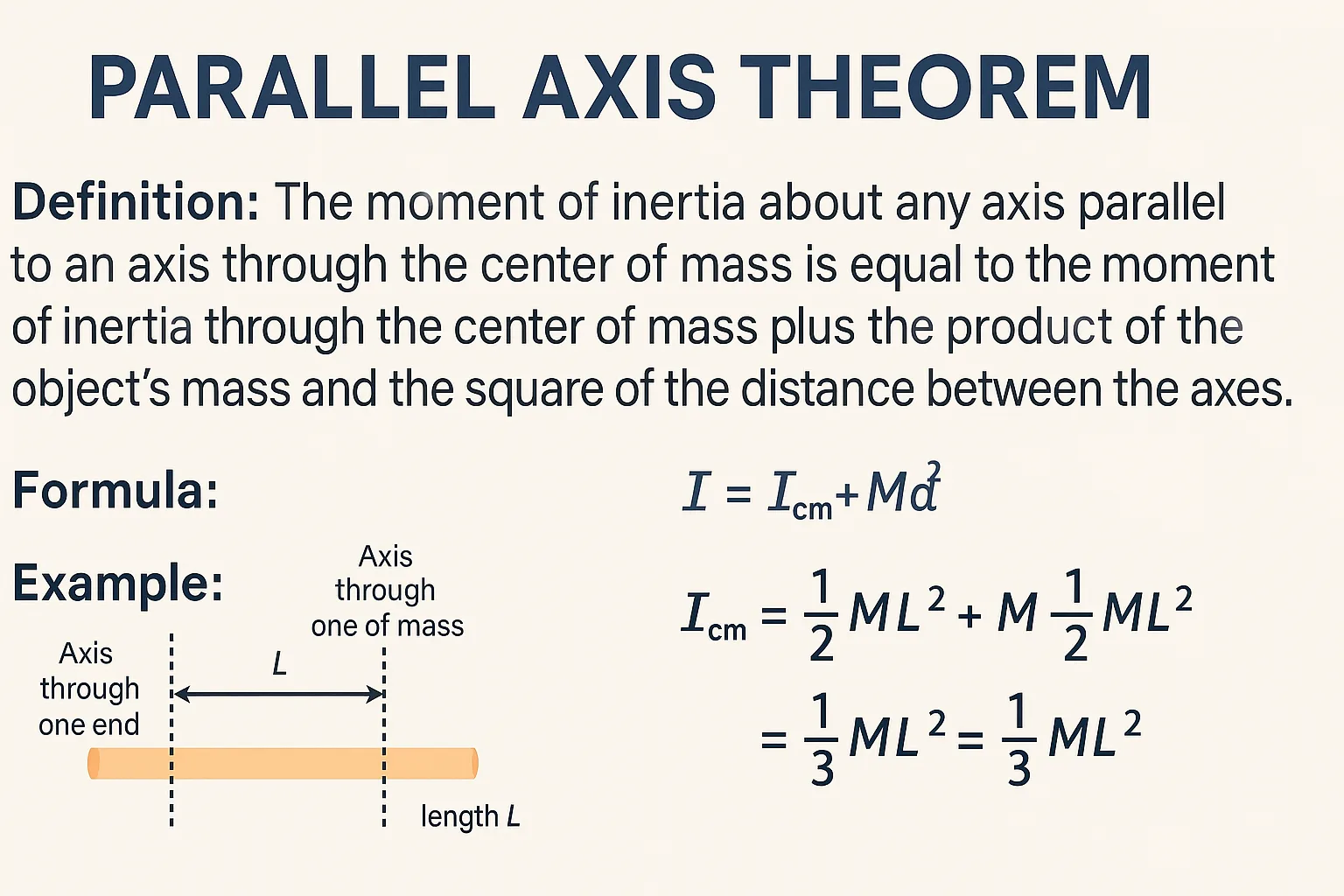
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
