
An Arabic word is a term or expression that originates from the Arabic language, one of the oldest and most widely spoken languages in the world. Arabic is a Semitic language primarily spoken in the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of the Arabian Peninsula. It is also the liturgical language of Islam, as the Quran is written in Classical Arabic.
Characteristics of Arabic Words
- Root System:
- Most Arabic words are derived from a root system, typically consisting of three or four consonants. These roots convey a core meaning.
- Example: The root k-t-b relates to writing. From this root:
- Kitab (كتاب) = Book
- Kataba (كتب) = He wrote
- Maktab (مكتب) = Office or desk
- Writing Style:
- Arabic is written from right to left in a cursive script.
- It has 28 letters, and the shape of each letter changes depending on its position in the word (beginning, middle, or end).
- Complex Morphology:
- Words often include prefixes, suffixes, and infixes to indicate tense, gender, number, and case.
- Rich Vocabulary:
- Arabic is known for its extensive vocabulary and synonyms, reflecting its rich literary and poetic tradition.
Common Examples of Arabic Words
- Salam (سلام) = Peace
- Habibi (حبيبي) = My beloved (often used as “dear” or “darling”)
- Shukran (شكراً) = Thank you
- Allah (الله) = God
- Qalam (قلم) = Pen
Importance of Arabic Words
- Arabic words have influenced many other languages, including Persian, Turkish, Urdu, Spanish, and Swahili, due to historical trade, conquest, and cultural exchange.
- They are integral to Islamic worship and prayer for Muslims worldwide.
Arabic is not just a language but a medium that carries centuries of culture, history, and spirituality.
Additional Insights
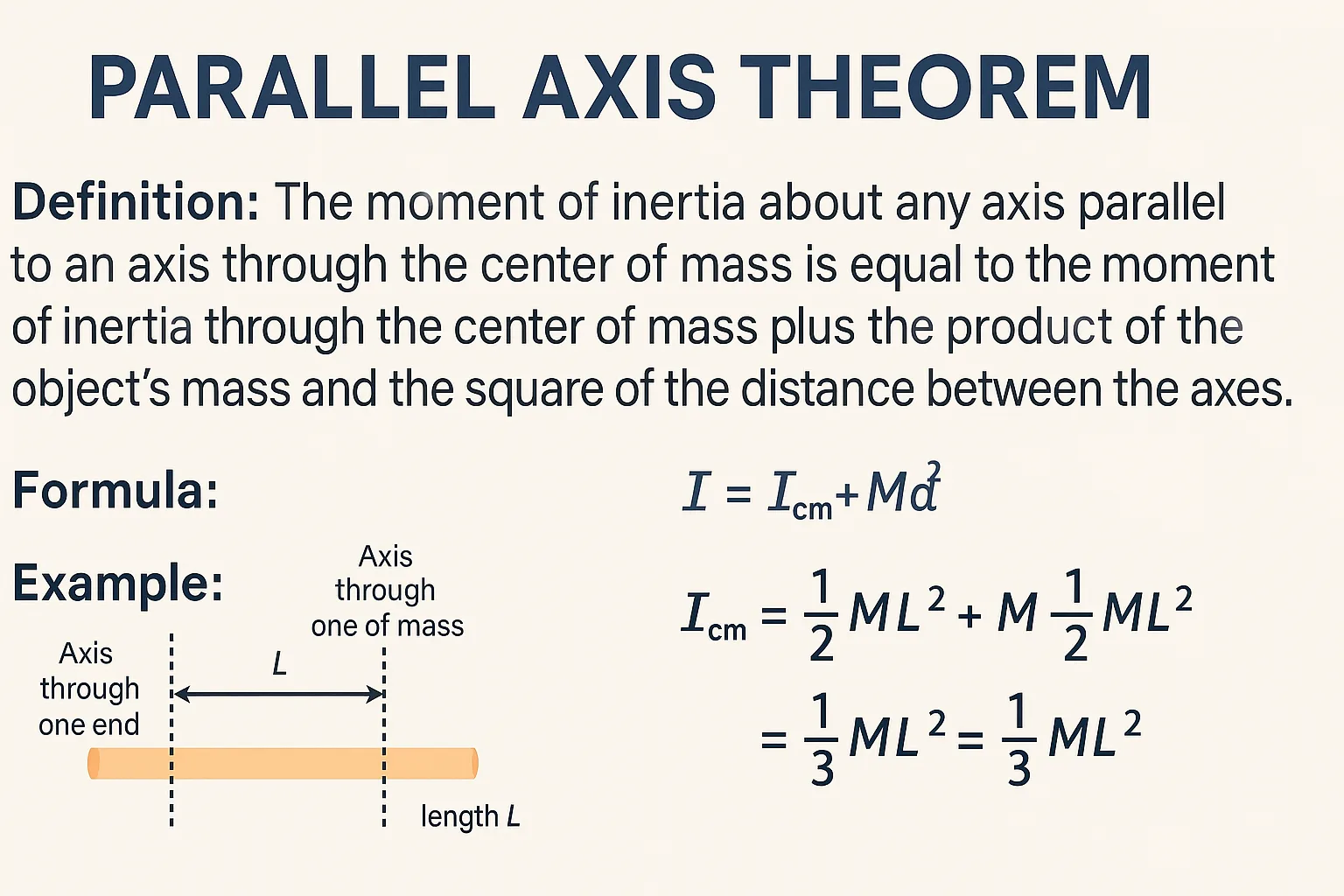
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
