What is EMI?

EMI, or Equated Monthly Installment, is a fixed payment amount made by a borrower to a lender at a specified date each calendar month. It is typically used in loans such as home loans, car loans, or personal loans. The purpose of EMI is to break down the loan amount into manageable monthly payments, ensuring that borrowers can repay their loans in an organized manner. The amount is calculated based on the principal loan amount, interest rate, and the duration of the loan. This helps borrowers plan their finances and avoid any lump sum repayments.
The EMI system is beneficial because it offers predictability, as the borrower knows exactly how much they need to pay each month, making it easier to budget. Additionally, since the EMI includes both the principal and the interest, the loan balance decreases over time. The interest is typically higher in the earlier stages of the loan, while the principal amount gradually increases as the loan term progresses. This structured repayment system ensures that both the lender and borrower have clarity throughout the loan tenure.
What are the types of EMI?
There are primarily two types of EMIs that borrowers can opt for, depending on the loan terms and conditions:
- Fixed EMI: In this type, the EMI amount remains constant throughout the entire loan tenure. The borrower pays the same amount every month until the loan is fully repaid. This is the most common type of EMI, providing predictability and stability for borrowers. Both the principal and interest portions are calculated at the start, so there are no surprises during the repayment period.
- Reducing Balance EMI: In this type, the EMI amount is calculated based on the outstanding loan balance. As the loan balance reduces with each payment, the interest component of the EMI decreases over time, while the principal portion increases. This method is more beneficial for those who plan to repay the loan faster, as the interest on the loan will be calculated only on the remaining principal.
Both types have their advantages depending on the borrower’s financial situation and repayment strategy. Fixed EMIs offer consistency, while reducing balance EMIs can save money on interest over time.
What is EMI calculator?
An EMI calculator is an online tool that helps borrowers calculate their Equated Monthly Installment (EMI) based on the loan amount, interest rate, and loan tenure. It allows users to easily determine how much they will need to pay each month to repay a loan. The calculator uses a formula that factors in the principal loan amount, the interest rate, and the duration of the loan to give an accurate EMI figure.
To use an EMI calculator, you typically need to input:
- Loan amount: The total amount you plan to borrow.
- Interest rate: The rate at which the lender will charge interest on the loan.
- Loan tenure: The duration of the loan, typically in months (e.g., 12 months, 36 months, etc.).
Once the details are entered, the calculator instantly provides the monthly EMI amount, helping borrowers plan their finances effectively. Some advanced EMI calculators also allow users to choose between fixed or reducing balance EMIs and even see the breakup of the principal and interest components of each installment.
What are the types of Loan?
There are several types of loans, each designed to serve different financial needs. Here are the most common types:
- Personal Loan: A personal loan is an unsecured loan, meaning you don’t need to provide collateral. It’s usually used for personal expenses like medical bills, home renovations, or weddings. These loans often have a fixed interest rate and repayment period.
- Home Loan: A home loan is a secured loan taken to buy, construct, or renovate a property. The property you purchase serves as collateral for the loan. Home loans typically have lower interest rates and longer repayment terms compared to personal loans.
- Car Loan: This is a secured loan used to buy a car or other vehicle. The vehicle itself acts as collateral for the loan, and if you fail to repay, the lender can repossess it. Car loans generally have a fixed interest rate and repayment tenure.
- Education Loan: Education loans are designed to help students pay for their higher education, including tuition fees, books, and living expenses. They can be unsecured or secured, depending on the lender, and they often have a flexible repayment schedule that begins after graduation.
- Business Loan: A business loan is used by entrepreneurs to start or grow their business. It can be secured or unsecured and is typically used for purchasing equipment, covering operational costs, or expanding a business.
- Credit Card Loan: A credit card loan allows you to borrow money up to your credit limit for purchases. The borrowed amount must be paid back along with interest, and the lender may offer the option of paying in installments.
- Home Equity Loan: A home equity loan is a secured loan where you borrow against the equity in your home. It can be used for any purpose, like home improvements or debt consolidation. The interest rates are generally lower since the loan is secured by your property.
- Payday Loan: A payday loan is a short-term, high-interest loan meant to cover urgent expenses until your next payday. These loans are usually small amounts and should be repaid quickly.
- Gold Loan: A gold loan is a secured loan where you pledge gold jewelry or other gold assets as collateral. These loans are typically short-term, and the interest rates are lower than unsecured loans.
- Debt Consolidation Loan: This type of loan is taken to combine multiple debts into one loan. It helps simplify repayment by merging various debts into a single monthly payment, often at a lower interest rate.
Each type of loan serves different purposes and has its own set of terms, interest rates, and repayment conditions. Choosing the right loan depends on your specific needs, financial situation, and the purpose of borrowing.
Additional Insights
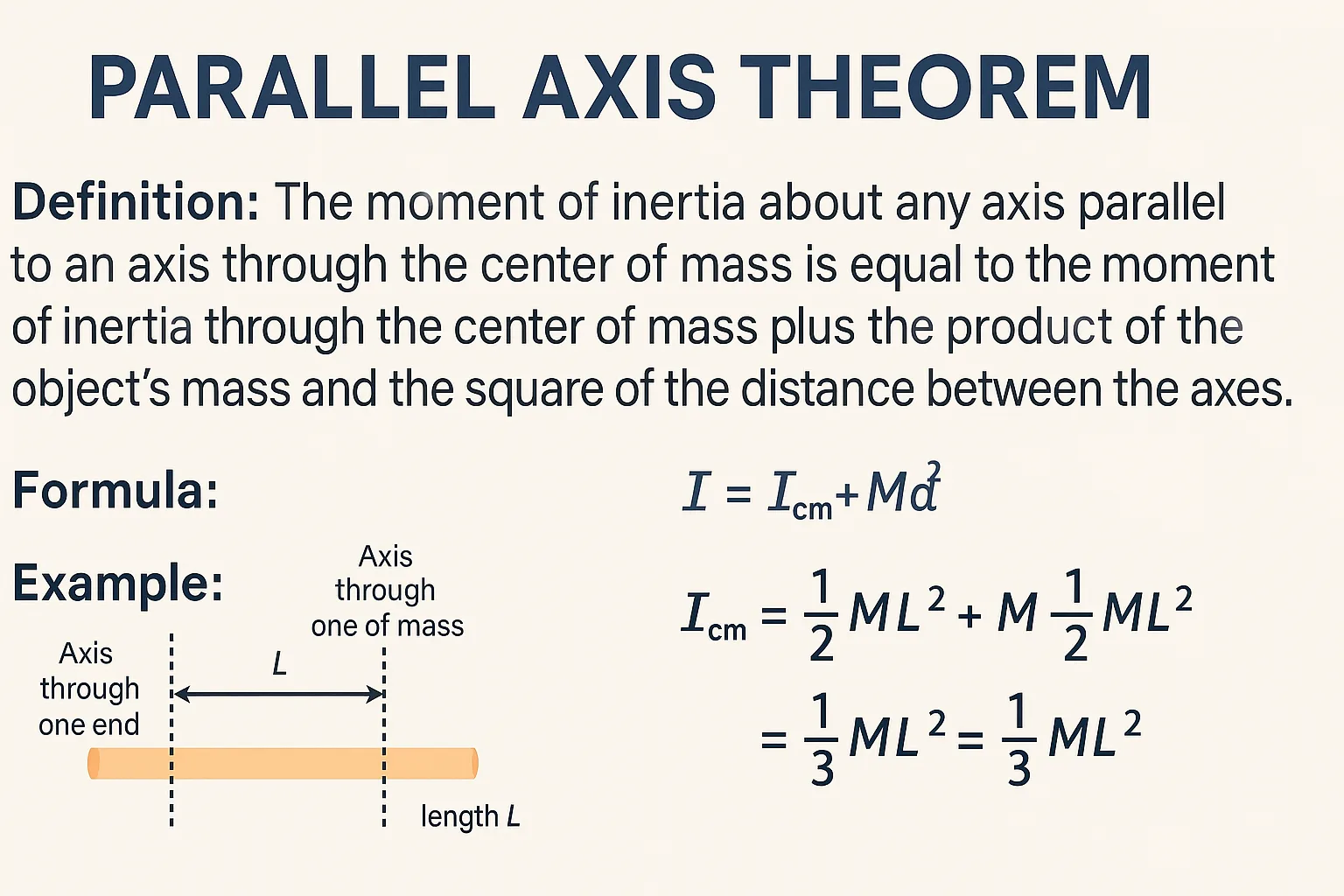
Parallel Axis Theorem – Definition, Formula, Derivation & Applications
Axis of Symmetry: Definition, Equation, and Real-Life Applications
X and Y Axis: Definitions, Graphs and Examples
Coconut Spanish Translation

Cashew Spanish Translation
Axis Definition and Meaning

Walnut in Spanish Translation

Almond in Spanish – Translation and Meaning
Recent Posts
- BlackBerry in Spanish
- Plum in Spanish
- Dragon fruit in Spanish
- Lemon in Spanish
- Academic word definition and meaning
